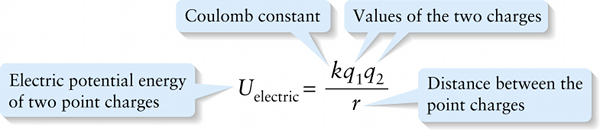
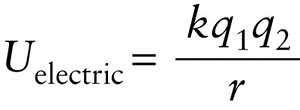Electric potential energy of two point charges (17-3)
Question 1 of 4
Question
Values of the two charges
{"title":"Electric potential energy of two point charges","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"3,36,38,76\"}]"} {"title":"Coulomb constant","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"186,1,207,44\"}]"} {"title":"Values of the two charges","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"227,24,228,24\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"212,14,234,50\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"251,15,278,52\"}]"} {"title":"Distance between the point charges","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"222,78,248,103\"}]"}Review
This expression is very similar to Equation 10-4 for gravitational potential energy. Equation 17-3 shows that \(U_{\mathrm{electric}}\) is inversely proportional to the distance \(r\), so the electric potential energy is zero when the two charges are infinitely far apart \(r \to \infty\)). But unlike gravitational potential energy, \(U_{\mathrm{electric}}\) can be either negative or positive depending on the signs of the two charges. If \(q_1\) and \(q_2\) have different signs (one positive and one negative) so that the two charges attract each other, then \(U_{\mathrm{electric}} < 0\) for any finite distance \(r\) between the charges (Figure 17-4b).