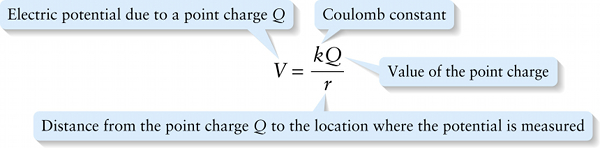
Chapter 17. Electric potential due to a point charge (17-8)
Question
y2idldHfHRAmBk381rCY0gIIW0X4qHCPUFhGSwwtPdsofcEnog4kL8mXHJ9ZZRdZPcnH6w==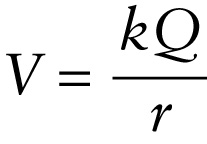
Question
O/vKXcQmzlU6zTGNJD/cTVj80sI=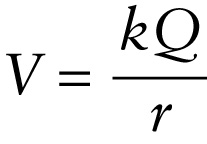
Question
RX+CRwZ3arLe0MfWLWP59GbtZFnJQHegu76DmKN/k2c=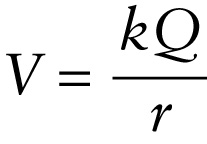
Question
Tba1ndhOkXvTgybXcV1yDPh8bEA6Avld0iE3RWSFTaU+lbnZzJkK9vE0ZM+b/yyBswl6nTj6L728BwF1d3RWJGizbyJYE4B//utbpSkLTTldF7xfgmMXtw==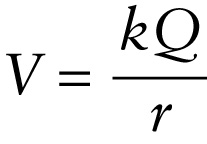
Review
Equation 17-8 says that all points that are the same distance \(r\) from a point charge have the same electric potential due to that charge. It also says that if \(Q > 0\), the electric potential due to the charge is positive and decreases (becomes less positive) as you move farther away from the charge so that \(r\) increases. If \(Q < 0\), the electric potential due to the charge is negative and decreases (becomes more negative) as you move closer to the charge. For either sign of \(Q\), the electric potential goes to zero at an infinite distance from the point charge.