Chapter 18. Power for a resistor (18-24)
Question
3QxhZQDQ+v7PQP5i1CxHMkd1Nah3d96AnwDEVA==
Question
MUUs2yh1zJAdGmNKxDUBqvbbc8u9otbaqEfLcMiEu/k=
Question
mMeCJb9LYec2D9sQzVDfFznir2p5Al8/VvdKHLmgcLA=
Question
Be2tWOBxdYEcD2Q3lcFQtZd/9iWt2NqbSFGqNvkPlwY=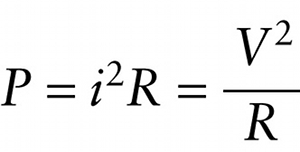
Review
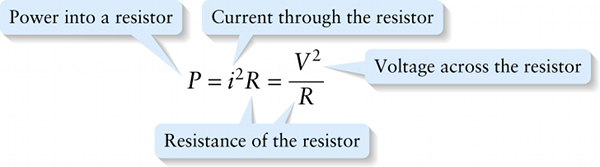
For the special case where the circuit element is a resistor with resistance \(R\), Equation 18-9 tells us that the voltage \(V\) across the resistor is equal to the product of the current and the resistance: \(V = iR\), or equivalently \(i = V/R\). We can use these two expressions to rewrite Equation 18-23 in two equivalent forms for the special case of a resistor:
\(P = i(iR)\) or \(P = \left(\frac{V}{R}\right)V\)
We can simplify these to