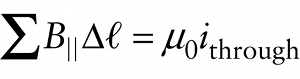Ampère’s law (19-13)
Question 1 of 3
Question
Current through the Amperian loop
{"title":"Circulation of magnetic field around an Amperian loop","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"41,18,66,52\"}]"} {"title":"Permeability of free space","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"159,27,186,58\"}]"} {"title":"Current through the Amperian loop","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"196,21,213,54\"}]"}Review
The circulation around any path that encloses the wire is equal to \(\mu_{0}i\). This is an example of Ampère’s law, which was discovered by the French physicist André-Marie Ampère (pronounced “ahm-pair”) in 1826:
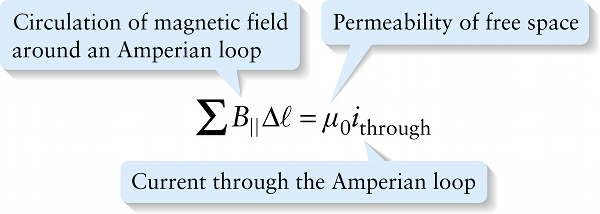
An Amperian loop is simply a closed path in space; the circle in Figure 19-20 is an example. The subscript “through” reminds us that the right-hand side of Equation 19-13 should only include current that passes through the interior of the Amperian loop.