Chapter 20. Faraday’s law and Lenz’s law for induction (20-3)
Question
xzpKO/F/zXwdkqyoUlcE9J3AAOSAaMeNCD0WbvcRNveV3B0mNsr+yg==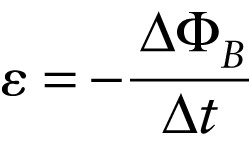
Question
FPeOmm2Hkz2wFl0xHELnGBC9huajwH7VTtuOd0t2RAKfW7pjGlA+oZugm54VJIhYmmIg8QhZ/4G9YI/6PzKHf+IUEznzfl10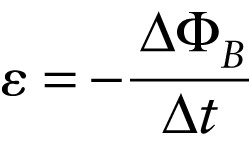
Question
ANTPJu2UK12DFGKgtM+5KPaaQmVuFNmz8cvIsPUcAJzn066Q9COL4SAbkP4g7I6UdYuDv9Fkrr+XKkWFM6/y97cSEOE=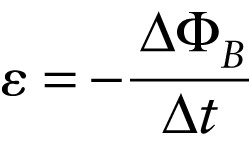
Question
cO2beNChBfIuSpjwu7vGPTCJZumI9T6GaGhH/qlY9ts7Hy8H1rqrKxmjTOtxjDPgChcFJax8sIaTJGTk8P26nmfggsmP8LiV2ikyHpY9TilxcxkMLL+nAvoI+VJ+z1/M/1c5lszrXextwd2MiCYuli1lNEFJASNZaeNzlg==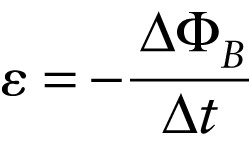
Review
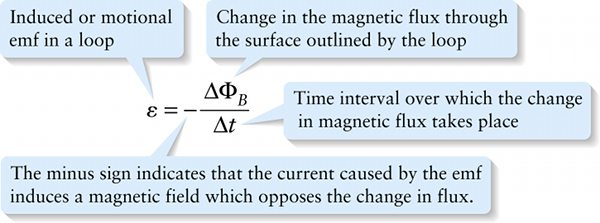
The nineteenth-century Russian physicist Heinrich Lenz summarized these observations in a principle that we now call Lenz’s law:
The direction of the magnetic field induced within a conducting loop opposes the change in magnetic flux that created it.
It’s common to combine Faraday’s law and Lenz’s law into a single equation: