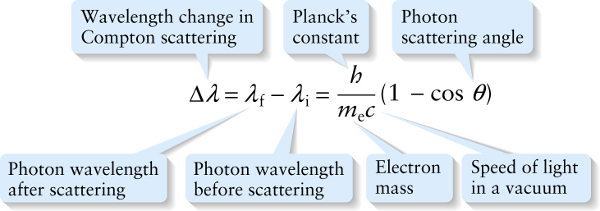
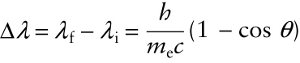Compton scattering equation (26-8)
Question 1 of 7
Question
Photon scattering angle
{"title":"Wavelength change in Compton scattering","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"16,18,31,43\"}]"} {"title":"Planck’s constant","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffff00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"157,1,173,23\"}]"} {"title":"Photon scattering angle","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#00ff00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"278,16,296,42\"}]"} {"title":"Speed of light in a vacuum","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#ff0000","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"172,41,188,56\"}]"} {"title":"Electron mass","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#800080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"145,37,167,58\"}]"} {"title":"Photon wavelength before scattering","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#0000ff","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"99,19,118,43\"}]"} {"title":"Photon wavelength after scattering","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#000000","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"52,18,72,42\"}]"}Review
Because a photon has less energy after a collision than it had initially, \(E_{\mathrm{f}}\) is less than \(E_{\mathrm{i}}\), and the final wavelength \(\lambda_{\mathrm{f}}\) is greater than the initial wavelength \(\lambda_{\mathrm{i}}\). In other words, as the nergy of a photon decreases, its wavelength increases.