Chapter 27. Binding energy of a nucleus (27-2)
Question
5fClfRGunV4XTy5HJLzj/hiJZ/ZOZcvx75pt/I5Ncbc=Question
hlxallnfXm6rXnGtvIv4uu4qgCAQDKCO0OlPdhfADTUcgDsKrZ953g==Question
yvvfujsY7PtpMcuFQkqDt79ntQ3H44yAeZZT1pIlTGhuREpHQuestion
a1Cn0zcVgaNAfsew6yn6A4RC9BZWd8gjCTxQdpEX0uvyShl/R/MbqI6ESA7GsZOm5HwgoCYegbORKj11Sd8kI/ShUCET+Gj+Question
bPc1Yg7xoR7yKjhmbmrt4oWiBz5cnkvqFSFY9UDw4ZQ=Question
gaEThimIcheyeBMCIB0tau47rMUY2nFIdPlu7Li92Z4oPv0rEdTkPJHPbbuDUSD9ZB3r+R1gJ2mKgKpiQuestion
e1qdm99yfR0B/CGF7E+kk6V4ifZtiTkKReview
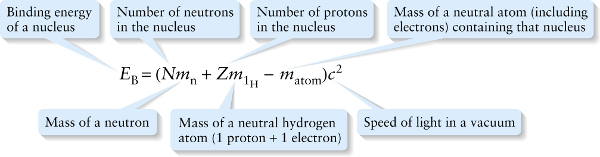
To find the binding energy of \(\sideset{^4}{\mathrm{He}}{}\), we subtracted the mass of the nucleus from the mass of the two protons and two neutrons separately, and then multiplied by \(c^2\) to find the equivalent energy. In general, for a nucleus consisting of \(N\) neutrons and \(Z\)protons, \(E_{\mathrm{B}}\) is
\(E_{\mathrm{B}} =\left(N m_{\mathrm{n}} + Zm_{\mathrm{p}} - m_{\mathrm{nucleus}}\right)c^2\)
where \(m_{\mathrm{n}}\) is the mass of a neutron, \(m_{\mathrm{p}}\) is the mass of a proton, and \(m_{\mathrm{nucleus}}\) is the mass of the nucleus. In practice, it’s easier to measure the masses of neutral atoms (including their electrons) than the masses of isolated atomic nuclei. In terms of these masses, we can write the binding energy of a nucleus as