Bubble Equation prototype
Question 1 of 3
Question
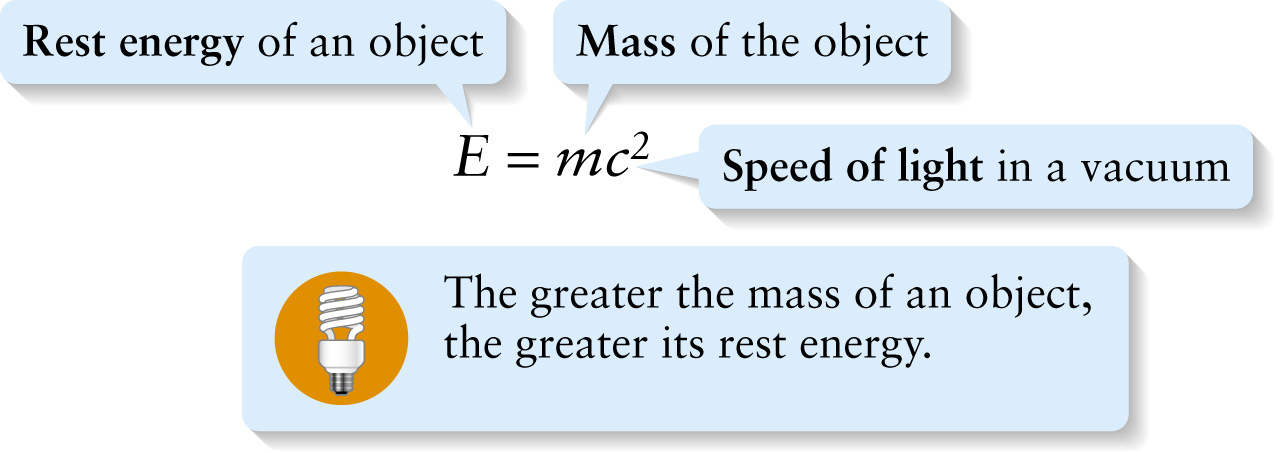
\(\textbf{Speed of light}\) in a vacuum
{"title":"Energy","description":"no","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"67,26,120,76\"}]"} {"title":"Mass","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#993300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"165,30,201,72\"}]"} {"title":"Speed of light","description":"YEah","type":"correct","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"196,30,226,70\"}]"}Review
In this equation \(E\) represents energy, \(m\) represents mass, and \(c\) represents the speed at which light travels in a vacuum. But what the equation means is something deeper. In this book we’ll often write fundamental equations with explanations attached, such as this one.