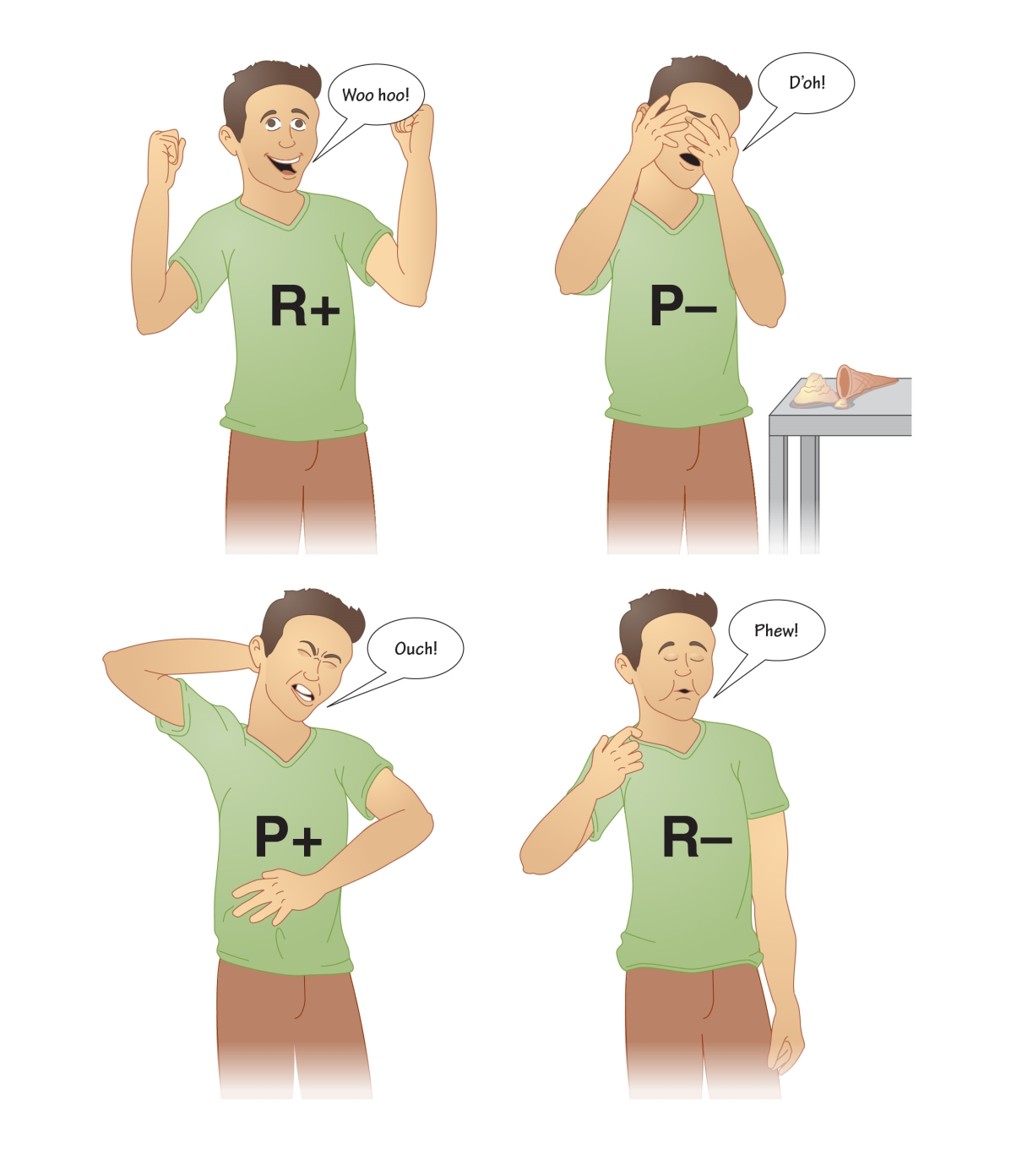
In operant conditioning, the learner forms a link between a particular behavior and the consequences that follow the behavior. Pleasant consequences are reinforcers; they strengthen the behavior and make it more likely to occur in the future. Unpleasant consequences are punishers; they reduce the likelihood that the behavior will be repeated.
Here are the four types of consequences. On the following screens you will see how each type of consequence influences the behavior of a rat in an operant conditioning chamber.