Appendix
Calculating Sums of Squares for One-Way Repeated-Measures ANOVA
Calculating sums of squares for a one-way repeated-measures ANOVA is quite similar to calculating sums of squares for a between-subjects, one-way ANOVA. Here are the pre-treatment, post-treatment, and follow-up distraction scores, squared and summed just as they were in Chapter 10 for a between-subjects, one-way ANOVA:
| Pre-Treatment | Post-Treatment | Follow-Up | ||||||
| X | X2 | X | X2 | X | X2 | |||
| Case 1 | 13 | 169 | 10 | 100 | 12 | 144 | ||
| Case 2 | 30 | 900 | 20 | 400 | 26 | 676 | ||
| Case 3 | 20 | 400 | 13 | 169 | 17 | 289 | Grand | |
| Case 4 | 26 | 676 | 17 | 289 | 20 | 400 | X | X2 |
| Sum | 89.00 | 2,145.00 | 60.00 | 958.00 | 75.00 | 1,509.00 | 224.00 | 4,612.00 |
| n | 4 | 4 | 4 | 12 | ||||
Once this is done, the values can be plugged into Equations 10.2, 10.3, and 10.4. SSTotal is calculated using Equation 10.2:
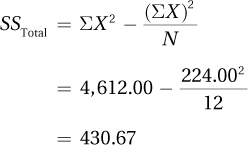
Next, we obtain SSBetween via Equation 10.3. This is called SSTreatment for repeated-measures ANOVA.
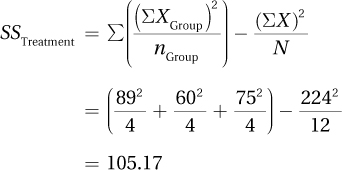
420
Then, using Equation 10.4, calculate SSWithin:
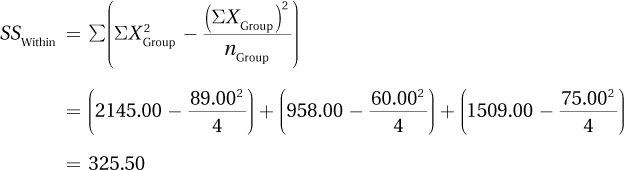
So far, all has been the same as for a between-subjects, one-way ANOVA. Now, it is time to diverge and calculate SSBetween. To do so, we need to add two new columns to the data table:
| Pre-Treatment | Post-Treatment | Follow-Up | ||||||||
| X | X2 | X | X2 | X | X2 | Case Total | T2/k | |||
| Case 1 | 13 | 169 | 10 | 100 | 12 | 144 | 35 | 408.33 | ||
| Case 2 | 30 | 900 | 20 | 400 | 26 | 676 | 76 | 1,925.33 | ||
| Case 3 | 20 | 400 | 13 | 169 | 17 | 289 | Grand | 50 | 833.33 | |
| Case 4 | 26 | 676 | 17 | 289 | 20 | 400 | X | X2 | 63 | 1,323.00 |
| Sum | 89.00 | 2,145.00 | 60.00 | 958.00 | 75.00 | 1,509.00 | 224.00 | 4,612.00 | 224.00 | 4,490.00 |
| n | 4 | 4 | 4 | 12 | ||||||
The two new columns are on the far right. The first, labeled “Case Total,” is the sum of all the scores for each case. For case 1, this is T = 13 + 10 + 12. The next column is that case total squared and then divided by k, the number of conditions. For case 1, this is 352/3. Note that all of these values are summed. SSSubjects is calculated:
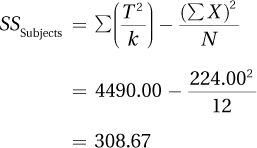
Finally, SSResidual is needed. SSResidual is what remains after SSSubjects is removed from SSWithin:
SSResidual = SSWithin – SSSubjects
= 325.50 – 308.67
= 16.83