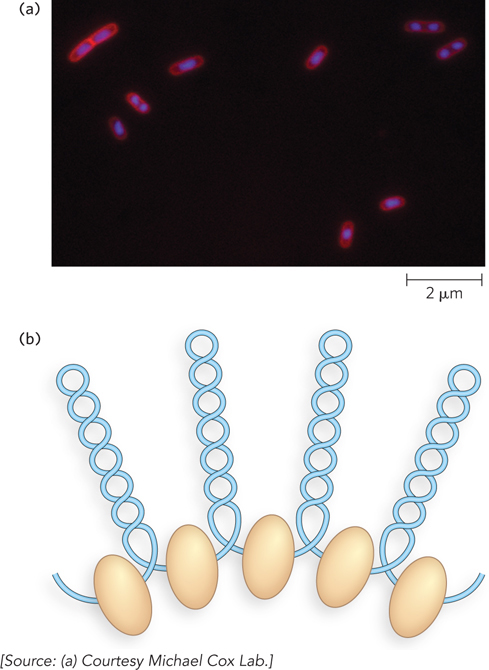
Highly condensed bacterial DNA. (a) The DNA is stained with a dye that fluoresces when exposed to UV light. The light areas define the nucleoids. Notice that some cells have replicated their DNA but have not yet undergone cell division and hence have multiple nucleoids. (b) Looped domains of DNA in the bacterial chromosome are separated by points of connection to the scaffold, shown as beige ovoids.