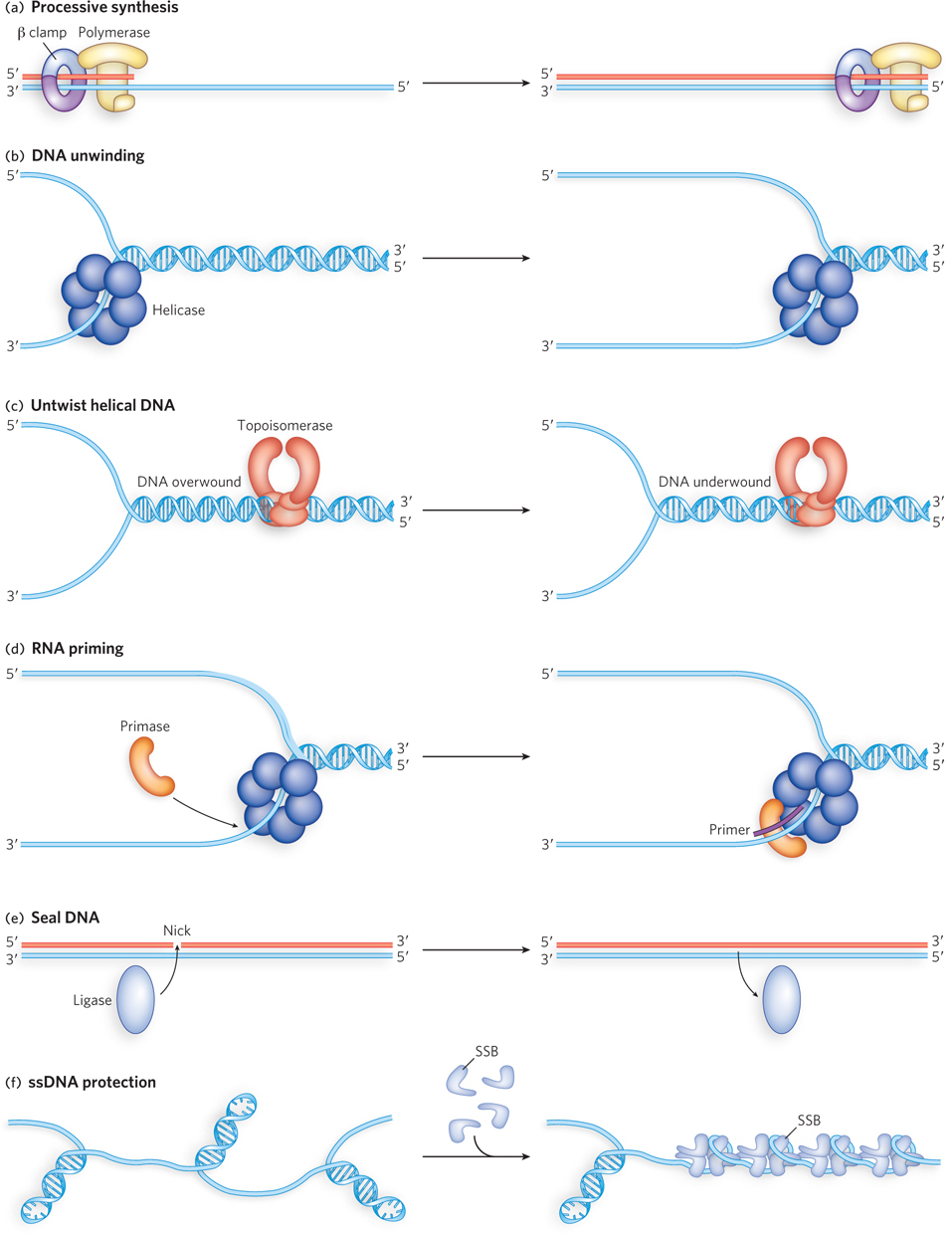
Activities required at a DNA replication fork. (a) DNA polymerase and the β sliding clamp are required for processive DNA synthesis. (b) Helicases that function at replication forks are hexamers that encircle single- e- A– e-