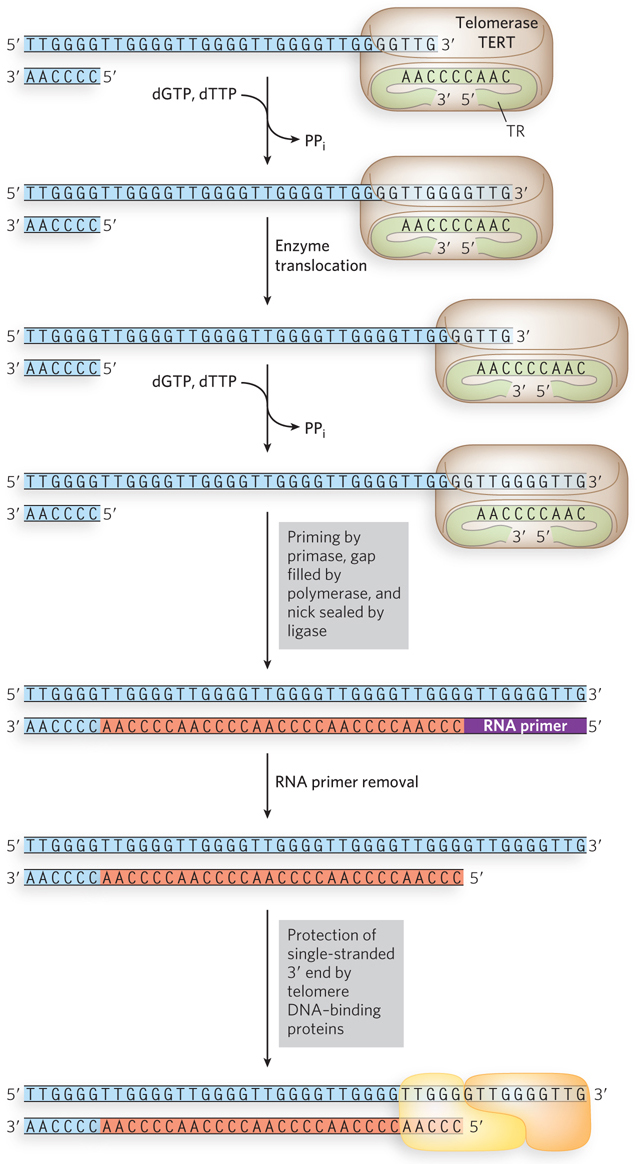
Extension of the ends of linear chromosomes by telomerase. Telomeres at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes are composed of a short repeating DNA sequence. Shown here is the repeating 5′-TTGGGG- e- l- e- A– e-