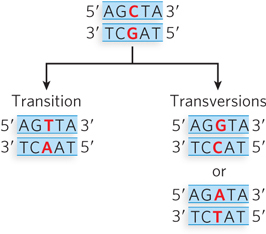
Transition and transversion point mutations. The parental DNA (top) contains a C≡G base pair. There are two possible point mutations: a transition (left), in which a purine (in this case, G) is replaced with a different purine (A), producing a T=A base pair on replication; or a transversion (right), in which a pyrimidine (in this case, C) is replaced with a purine (G or A) to produce either a G≡C or an A=T base pair. (To review hydrogen bonding between base pairs, see Figure 1-