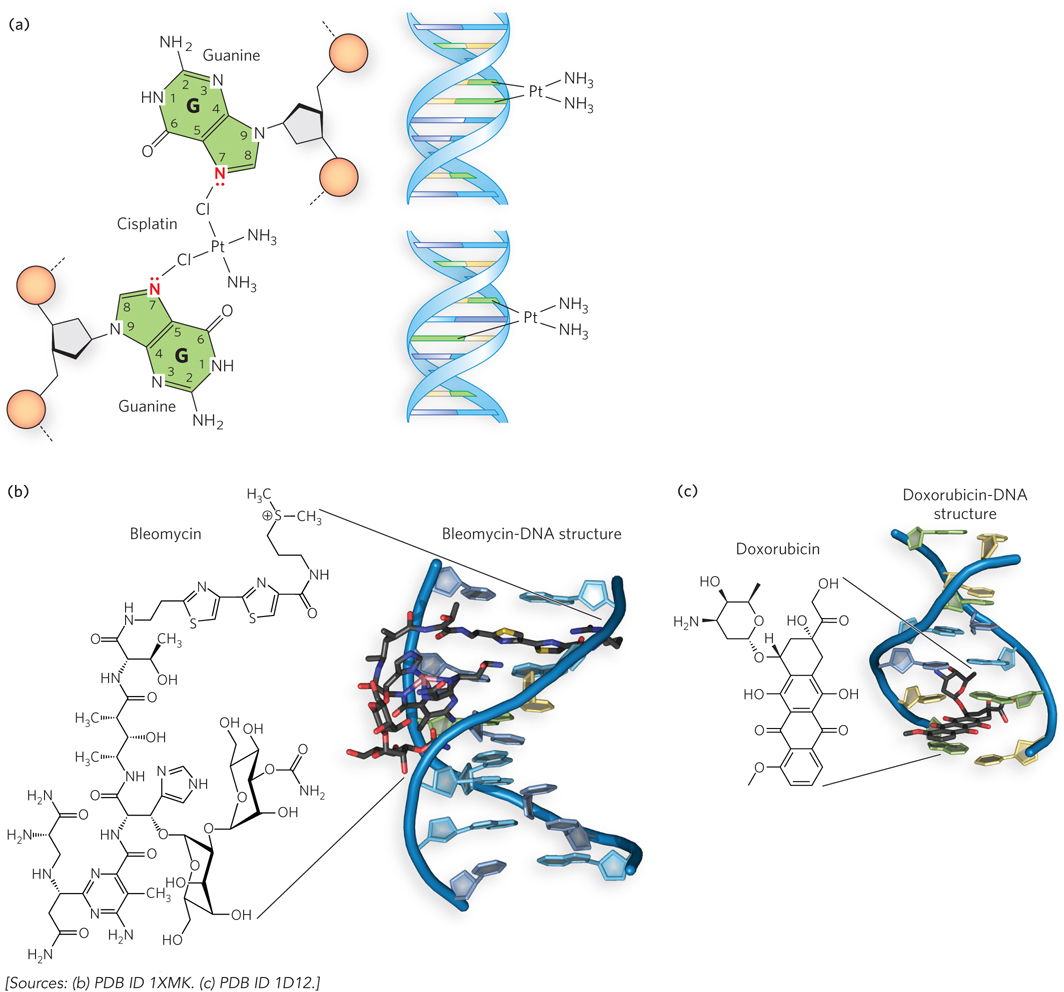
Chemotherapeutic DNA- t- s- N- s-