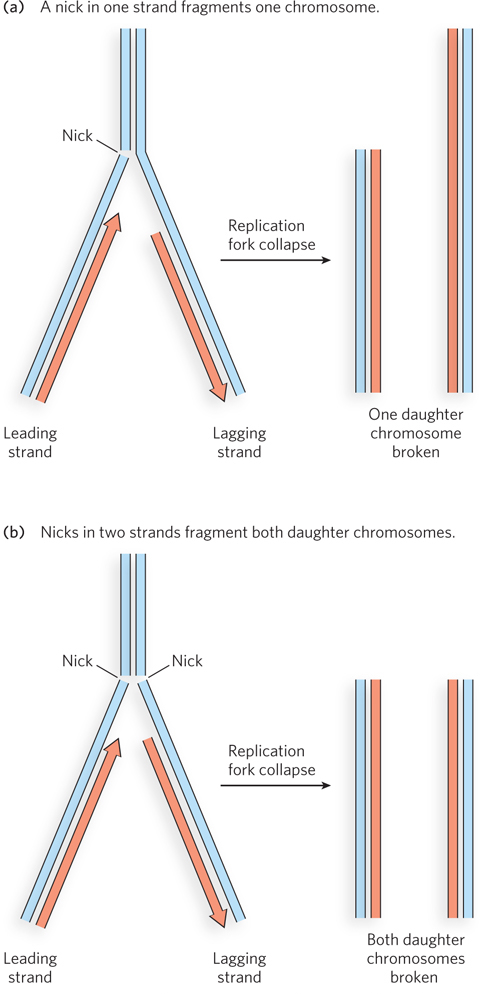
DNA damage caused by strand breaks during replication. (a) When a replication fork encounters a single-