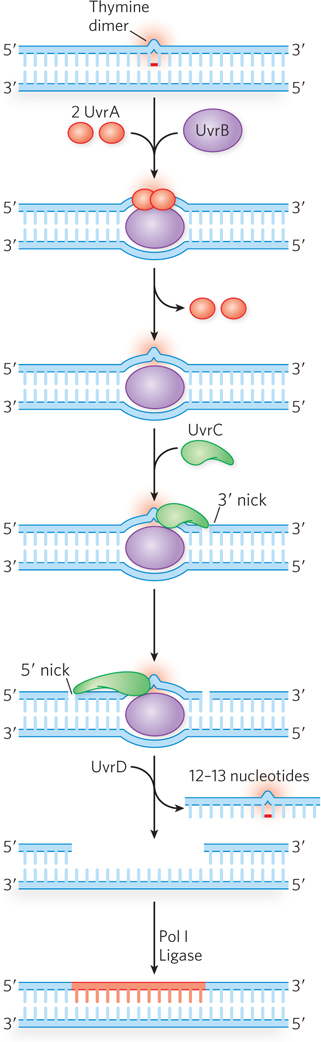
Nucleotide excision repair in E. coli. The NER pathway uses several proteins, including UvrA (red), UvrB (purple), and UvrC (green), that recognize the lesion and make incisions on either side, allowing UvrD (helicase II) to displace a section of lesion- e- n- A–