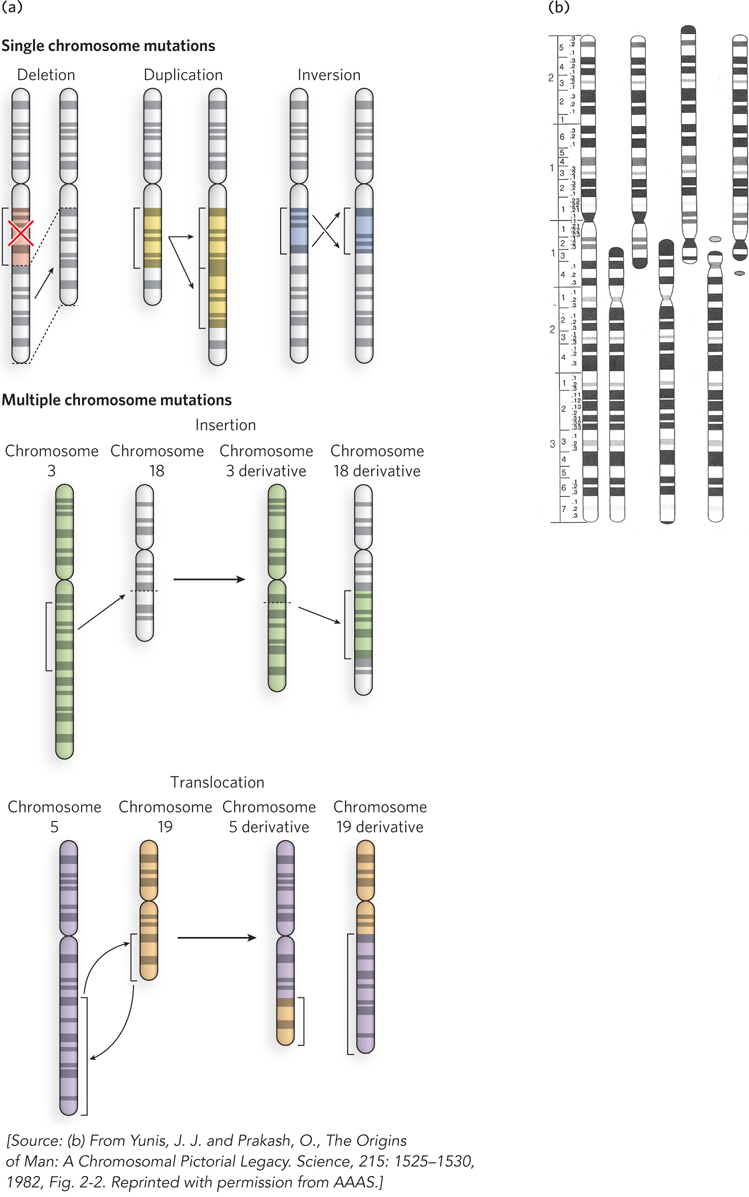
Large- 2—