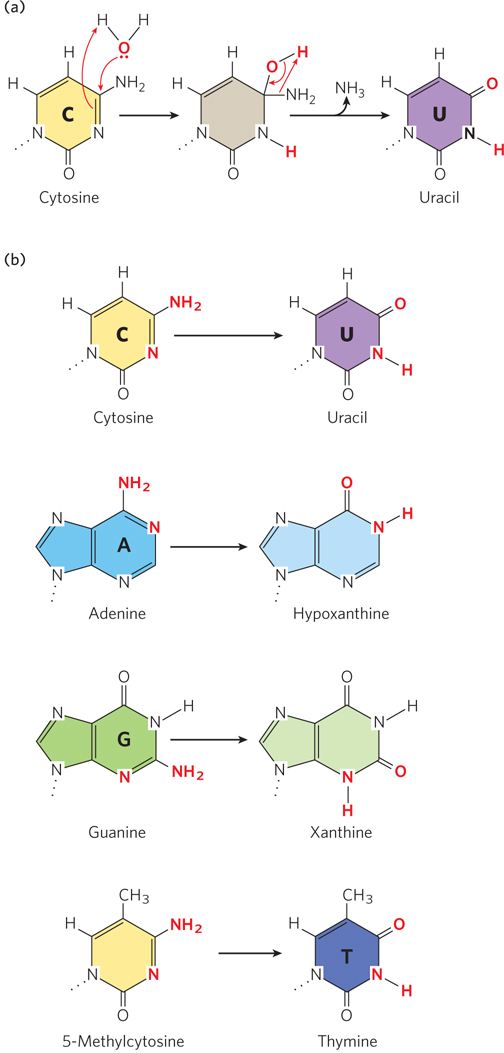
Deamination of nucleotide bases by spontaneous hydrolysis. In these deamination reactions, only the base is shown for each nucleotide residue. (a) A hydrolysis reaction in which water is added to cytosine, resulting in deamination to uracil and ammonia. A similar mechanism occurs in other deaminations. (b) Common deamination reactions resulting from hydrolysis of nucleotides in DNA.