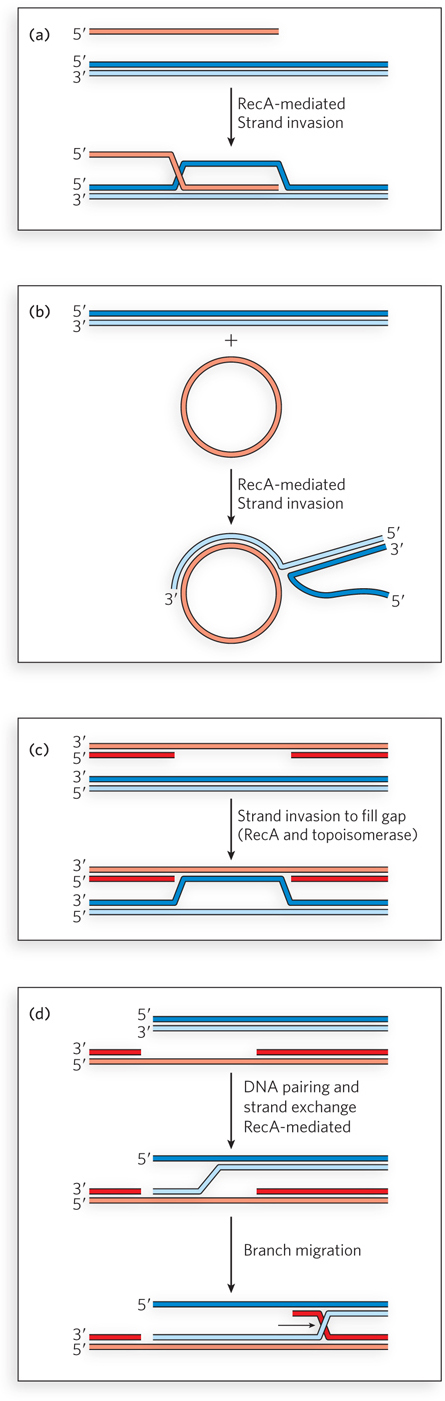
Recombination- e- D- 3- e- e- e- e- e-