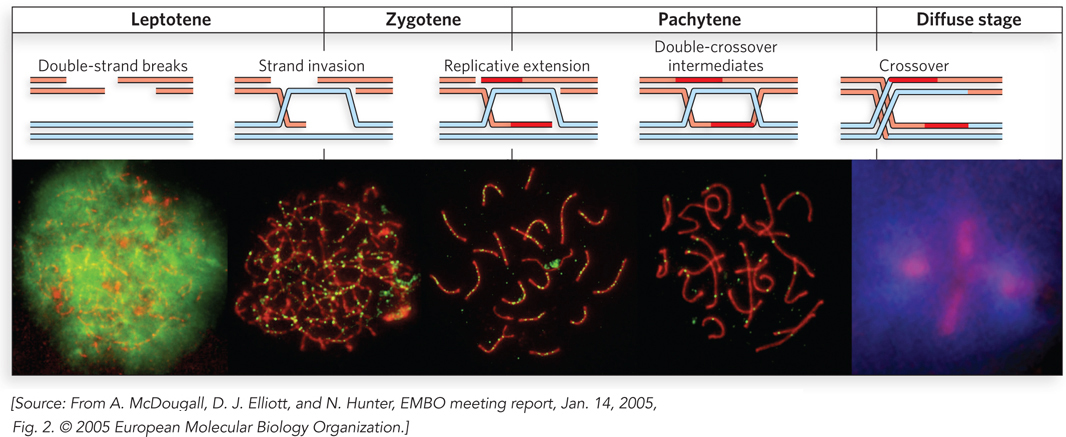
Homologous genetic recombination during meiotic prophase I. Prophase I includes a directed recombination process. The double- e-