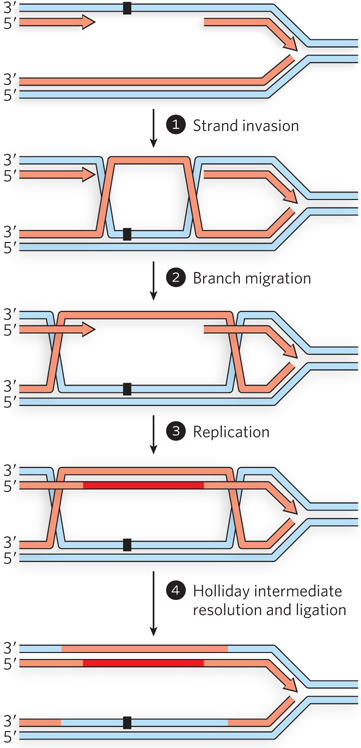
Repair of a DNA gap after the replication fork bypasses a lesion. If a single- e-