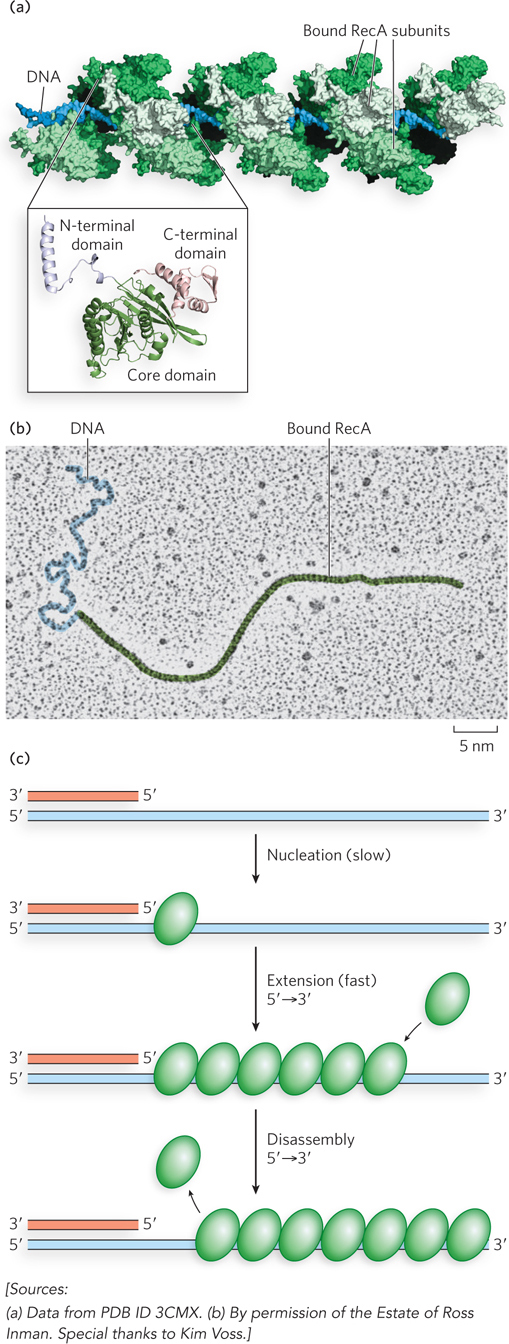
RecA protein filaments. RecA and other recombinases in this class function as filaments of nucleoprotein. (a) Segment of a RecA filament with four helical turns (24 RecA subunits). Notice the bound double-