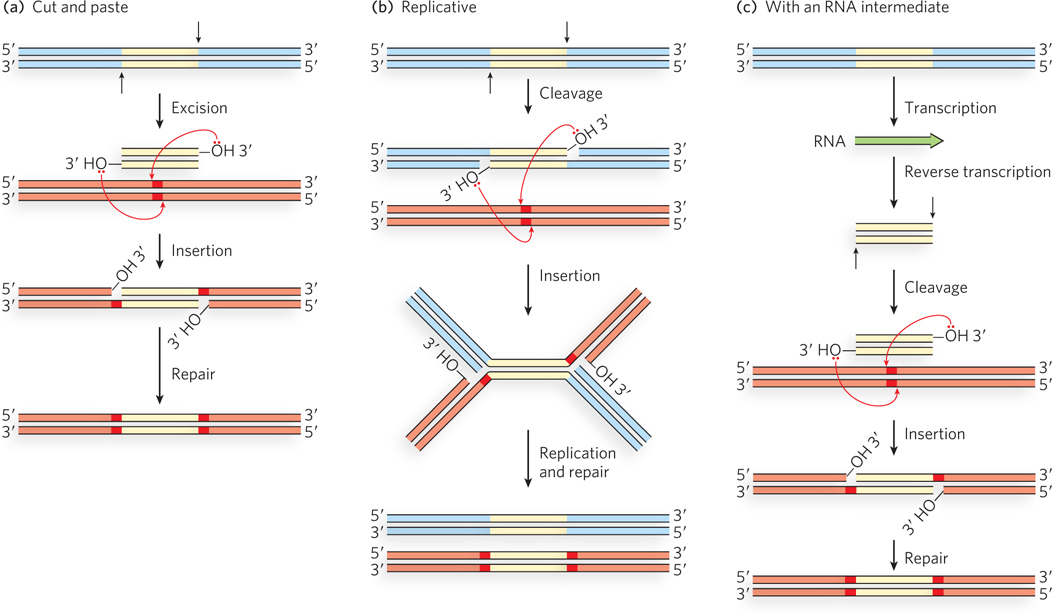
Three general transposition pathways. (a) Cut- d- e-