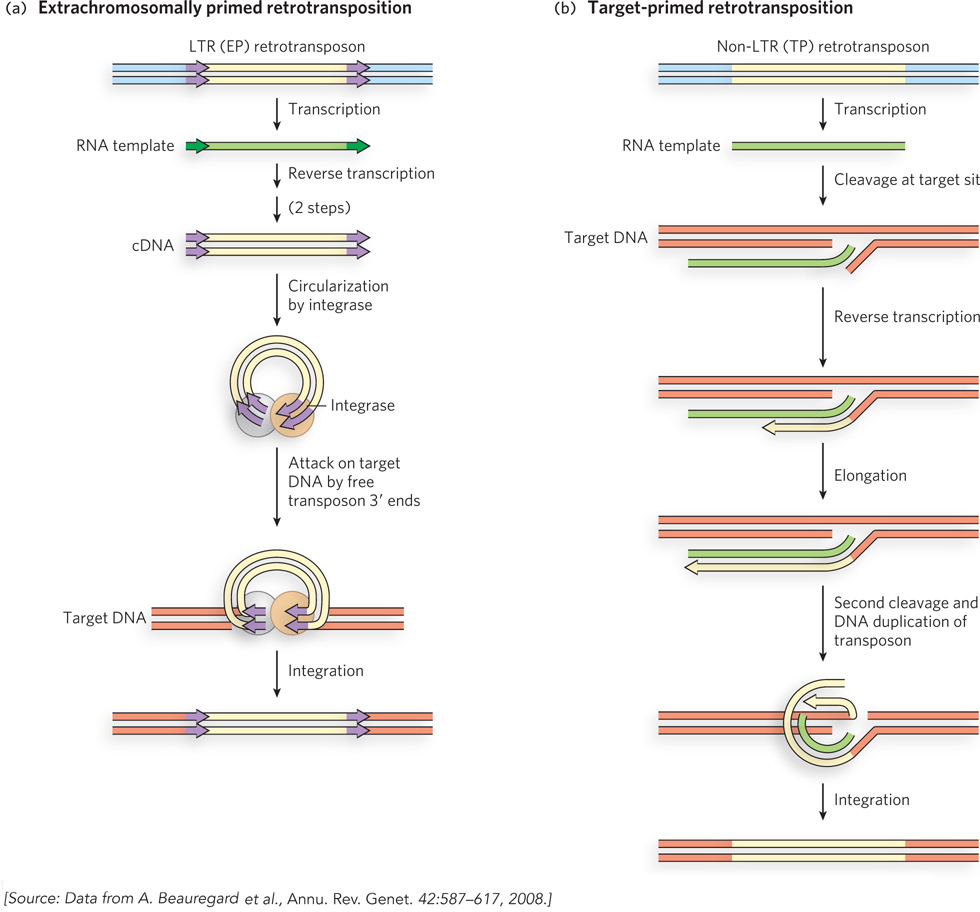
Retrotransposition. (a) In extrachromosomally primed (EP) retrotransposition, a tRNA or other RNA that can anneal to the transposon RNA is used as a primer for reverse transcription of the RNA to create a double- t- d- t- e-