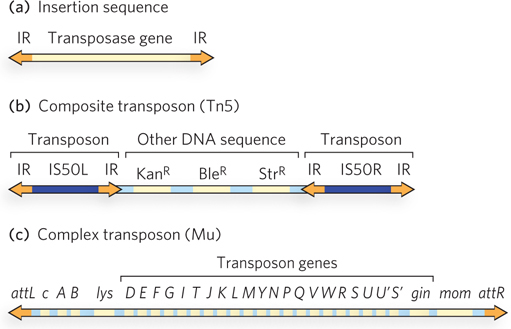
Three types of bacterial transposons. (a) Insertion sequences (IS elements) are the simplest transposons, consisting of a transposase- e- e-