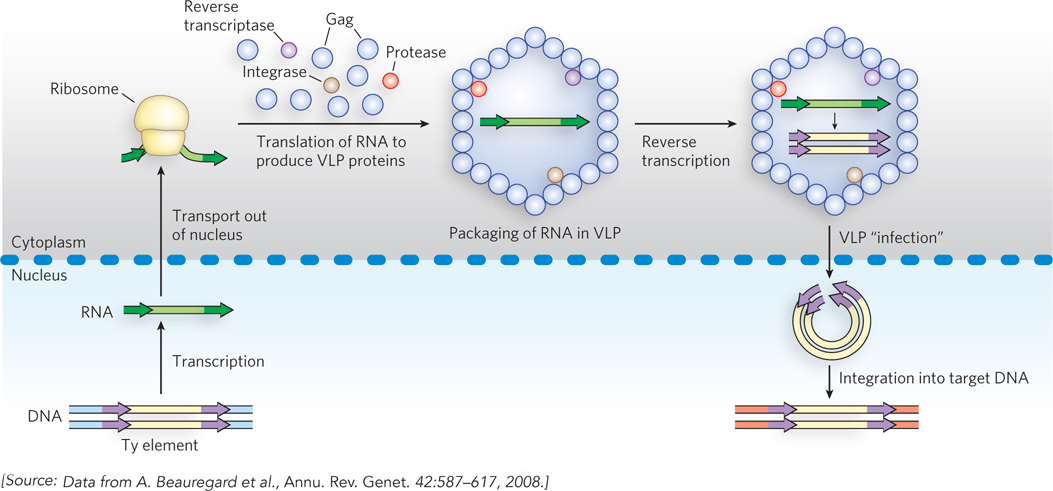
Retrotransposition by a Ty element in yeast. The Ty element, within the host DNA, is transcribed to produce an mRNA, which is transported to the cell cytoplasm and translated to produce a polyprotein (pol) that is cleaved to generate a protease, reverse transcriptase, integrase, and Gag (a structural protein). Within the viruslike particle (VLP), reverse transcriptase converts the RNA to double-