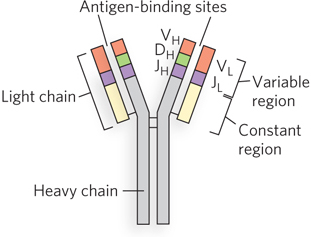
Immunoglobulin G (IgG). Pairs of heavy and light chains combine to form a Y- n-