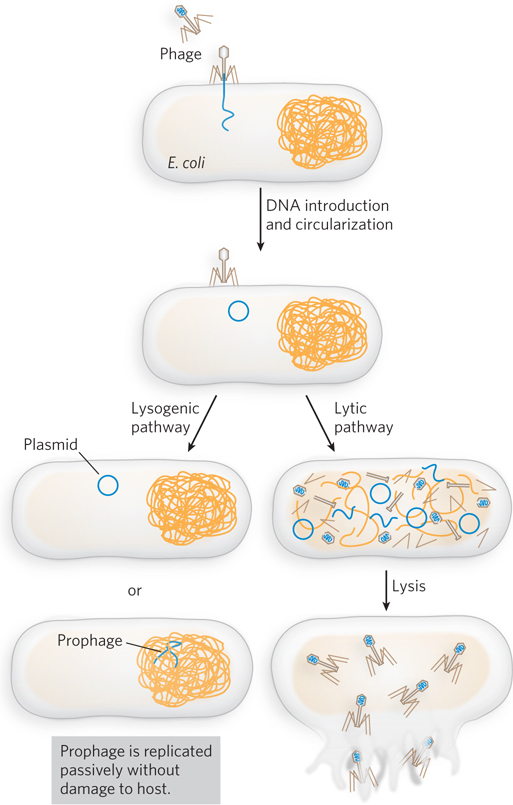
Two possible fates for a phage-