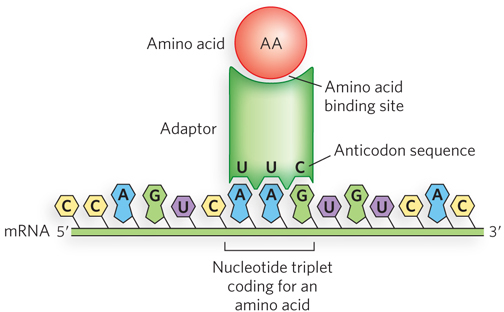
Crick’s adaptor hypothesis. Adaptor molecules recognize codons in mRNA and carry specific amino acids. Thus, they line up amino acids in an order that depends on the sequence of codons in the mRNA. Today we know that the adaptor is a tRNA molecule. The amino acid is covalently bound at the 3′ end of the tRNA molecule, and a specific nucleotide triplet (anticodon) elsewhere in the tRNA interacts with a triplet codon in mRNA through hydrogen bonding of complementary bases.