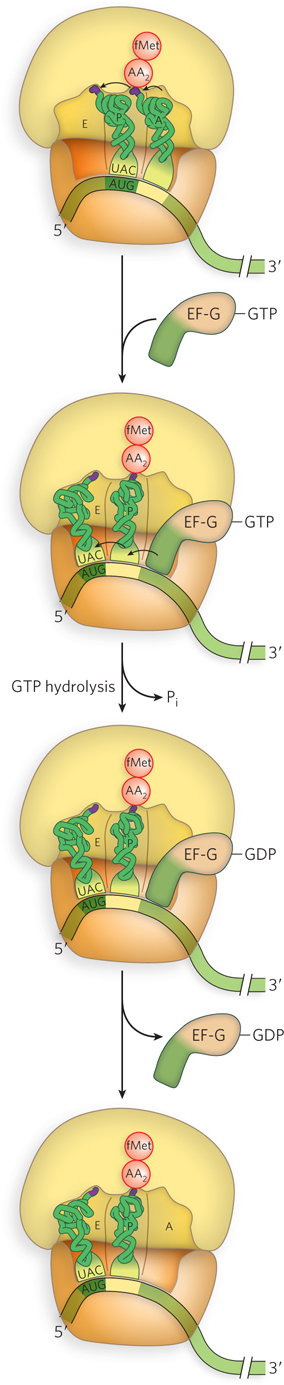
Translocation promoted by EF- 8- F- G– F- A- l- F- G– l-