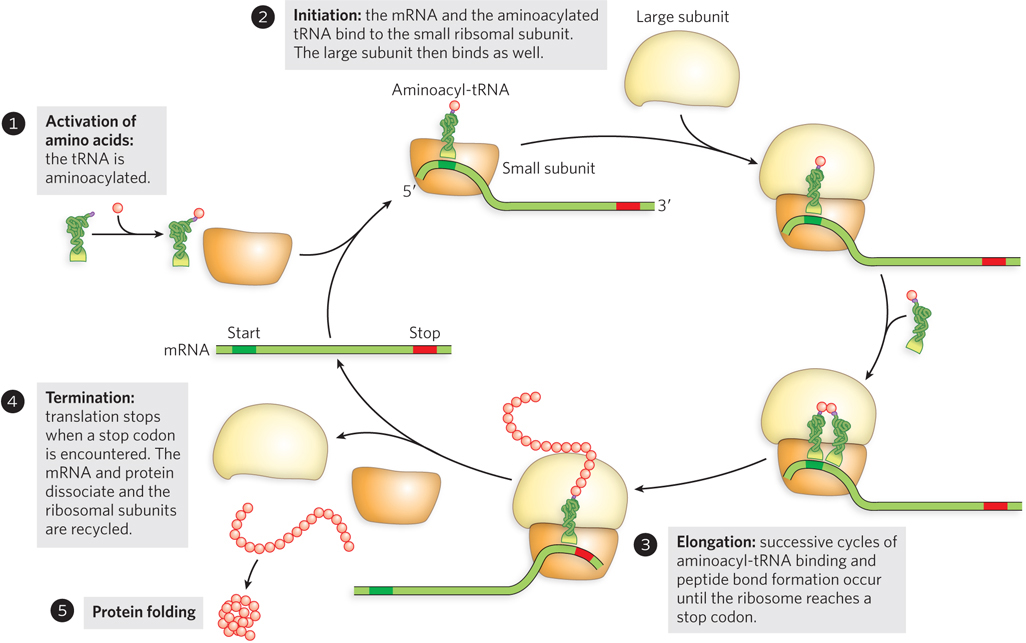
An overview of the main events in translation. Following the activation of amino acids by acylation to tRNAs (step 1), translation initiates with the assembly of mRNA and aminoacylated tRNA on the small ribosomal subunit, followed by joining with the large subunit to form an active ribosome (step 2). Polypeptide elongation occurs in successive cycles of aminoacyl-