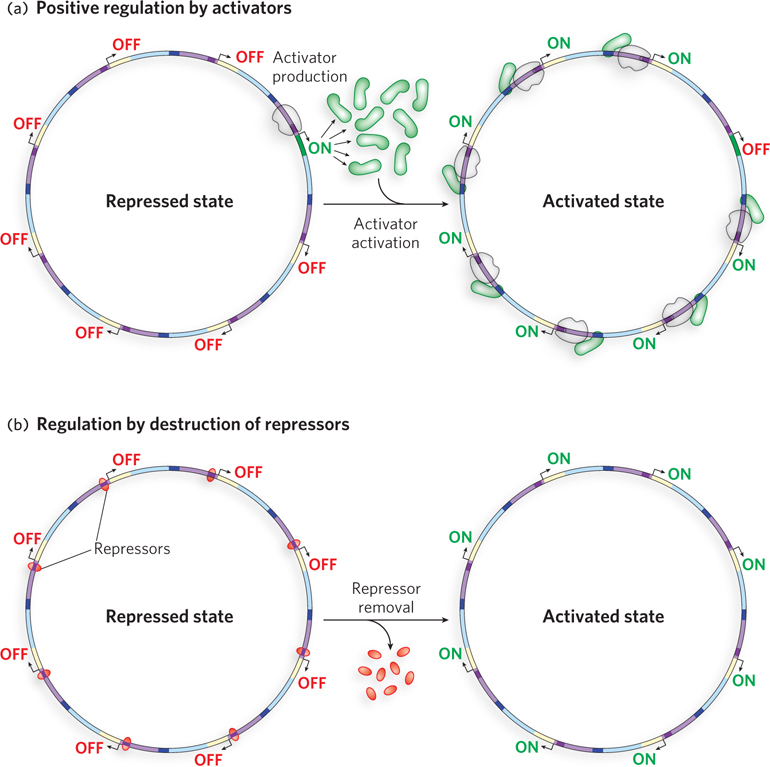
Global regulation of groups of genes. (a) Global regulation can occur through the binding of a common transcription activator. When needed, the activator may be produced de novo by expression of its gene, as shown, or an existing activator protein may become active for DNA binding through interaction with another protein or a small effector molecule. (b) Alternatively, global regulation can result from the removal of a common repressor bound to DNA sites, either by an allosteric change induced by binding of a small effector molecule or by proteolytic digestion of the repressor.