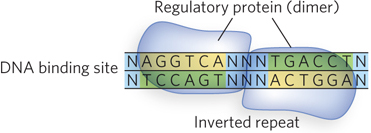
An inverted repeat at the site of transcription factor binding. A nucleotide sequence followed by the reverse, complementary sequence is known as an inverted repeat. It can have a variable number of base pairs that are not part of the repeat between the two repeated sequences. A palindrome is an inverted repeat with no base pairs between the two repeat sequences. Proteins that bind to inverted repeats are dimeric, and each subunit binds to one half of the repeat. Illustrated here is a homodimer binding an inverted repeat (N = any nucleotide).