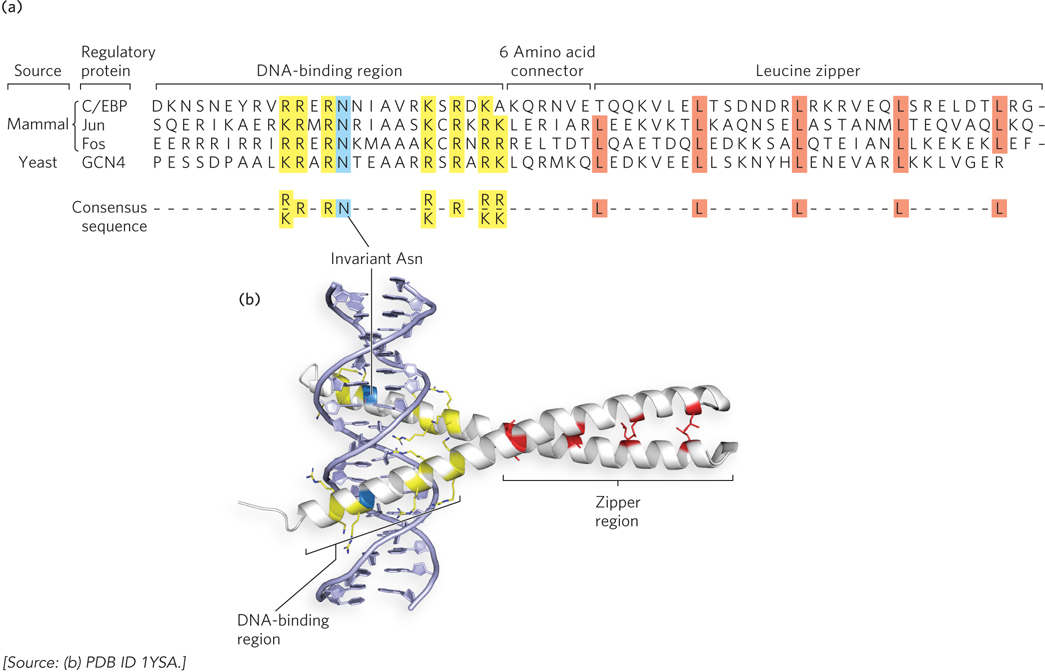
The basic leucine zipper motif. This motif is often used to mediate protein- s— A- d- A-