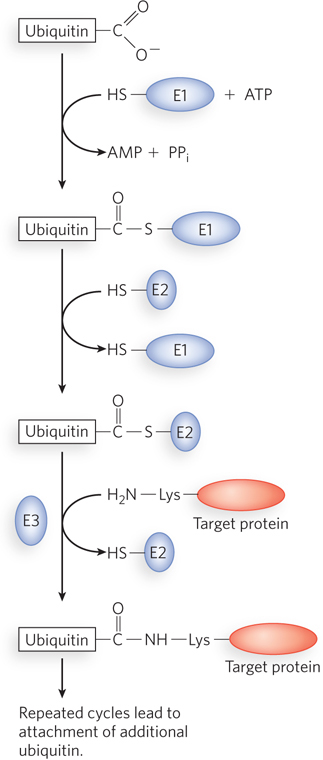
The protein ubiquitination pathway. In eukaryotes, three enzymes (denoted by E1, E2, and E3) carry out the polyubiquitination of proteins in a process that involves ATP and two enzyme- C-