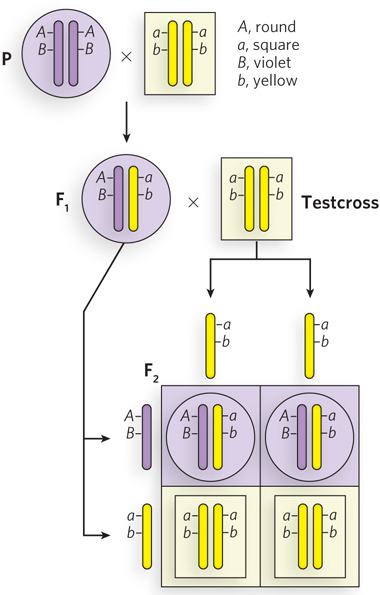
The inheritance of linked genes. Linked genes segregate together because they are on the same chromosome— e-