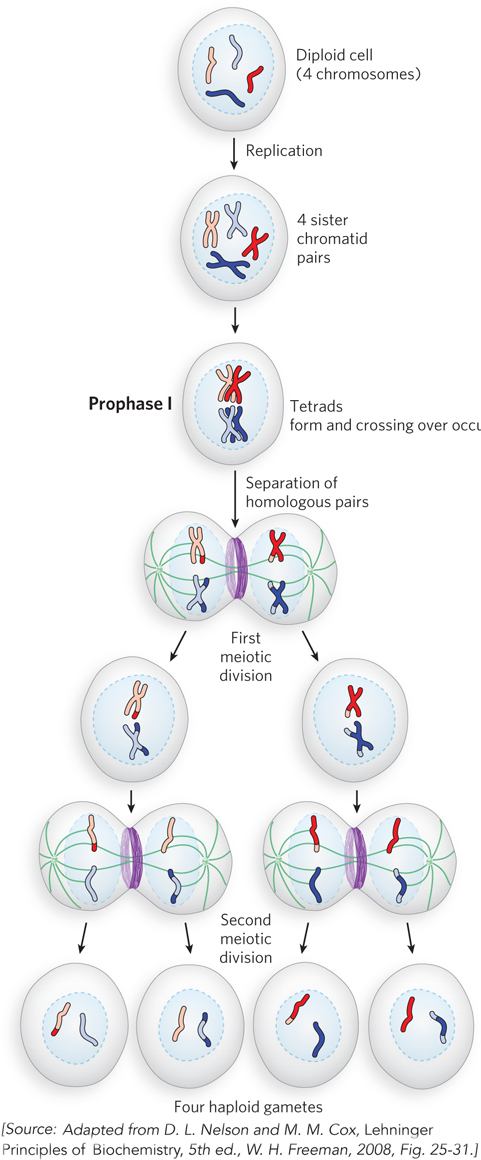
Recombination during meiosis. The chromosomes of a diploid cell (four chromosomes, two homologous pairs, are shown here) replicate, and each pair is held together at the centromere, forming four sister chromatid pairs. In prophase I, at the start of the first meiotic division, the two homologous sets of sister chromatid pairs align to form tetrads. Crossovers occur within the tetrads. In the first meiotic division, homologous pairs of chromosomes segregate into daughter cells. Each sister chromatid pair then lines up in preparation for the second meiotic division, which produces four haploid gamete cells. Each gamete has two chromosomes, half the number of the diploid cell.