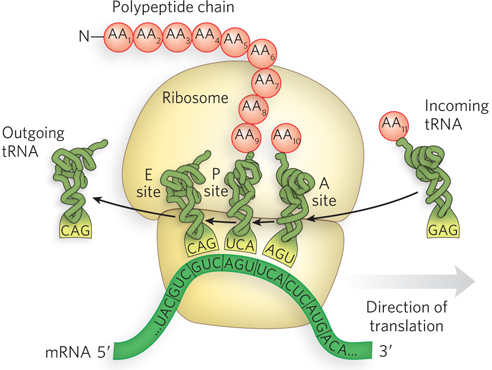
The process of translation. The ribosome, composed of a large and a small “subunit” (each consisting of many proteins and several rRNAs), mediates protein synthesis in cells. It associates with both mRNA and tRNAs as it synthesizes polypeptide chains. The ribosome has three major sites for binding tRNA molecules, the P site, the A site, and the E site. Two tRNAs form base pairs with their respective, adjacent, matching triplets on the mRNA: the tRNA in the P site carries the growing polypeptide chain, and the tRNA in the A site carries an amino acid (AA). The ribosome catalyzes the transfer of the polypeptide attached to the P- A- A- o-