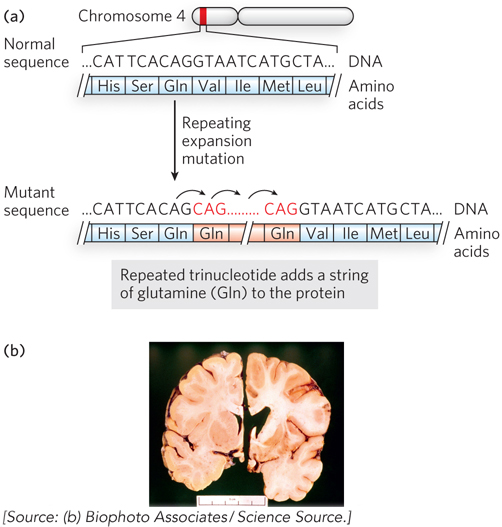
Huntington disease. Huntington disease is an inherited autosomal dominant neurological disease. (a) The gene for Huntington disease (HTT) is located on the short arm of chromosome 4, and the disease is associated with CAG repeats (CAG encodes glutamine) in this gene. When the number of CAG repeats increases above 36 copies, disease may occur in midlife. (b) Huntington disease affects the brain by causing degeneration.