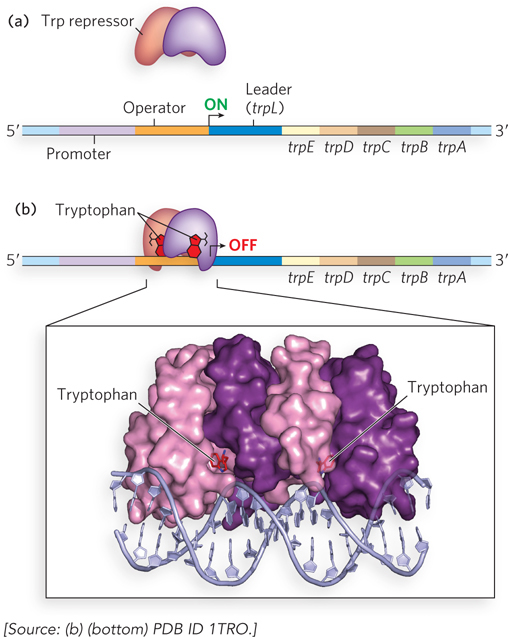
Regulation of the trp operon. (a) In the absence of tryptophan, the Trp repressor cannot bind the operator, and transcription of the trp operon is initiated. (b) When tryptophan is abundant, the protein products from the trp operon are no longer needed. Tryptophan serves as the effector molecule for the Trp repressor; their association causes the Trp repressor to bind the operator, blocking transcription. Notice the presence of the leader sequence; this is required for a second level of transcriptional control (see Figure 20-