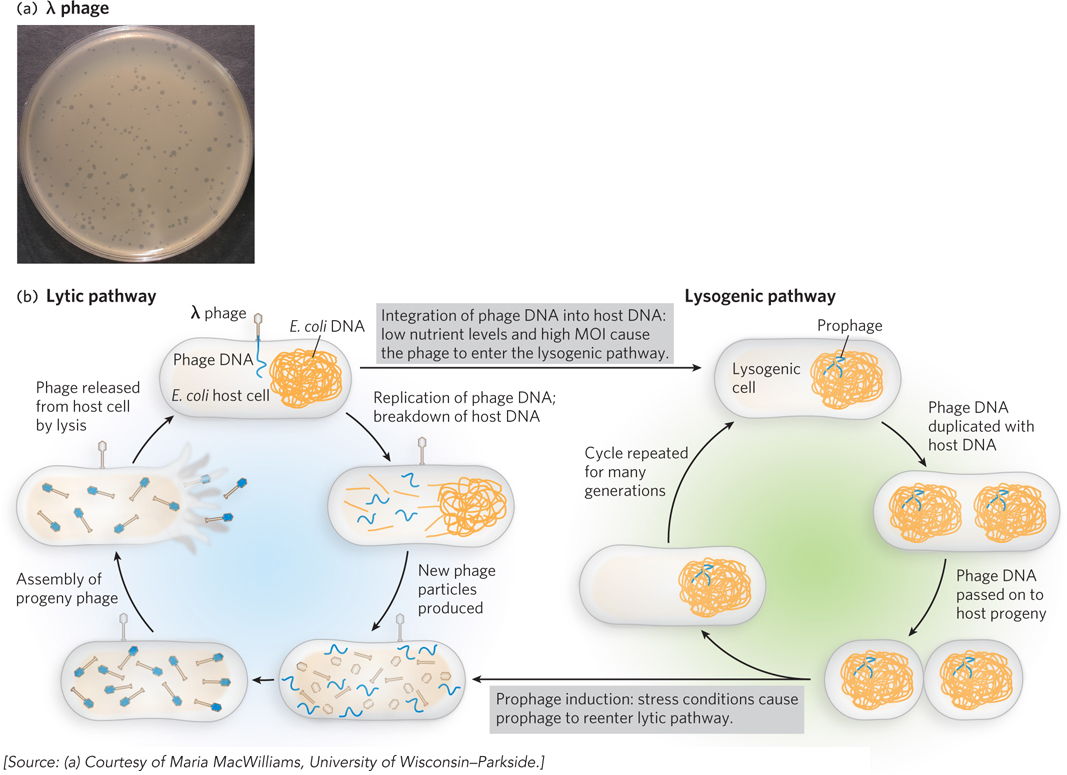
The growth and life cycle phases of λ phage. (a) Bacteriophage λ infecting a lawn of E. coli. The viruses eventually kill their host cells, leaving cleared spots, or plaques, in the bacterial lawn. (b) The lytic and lysogenic pathways. Use of the lytic versus the lysogenic pathway is based on cellular nutrients and the viral multiplicity of infection (MOI). Under conditions of cellular stress, λ phages can exit the lysogenic pathway and enter the lytic pathway, in the process of prophage induction.