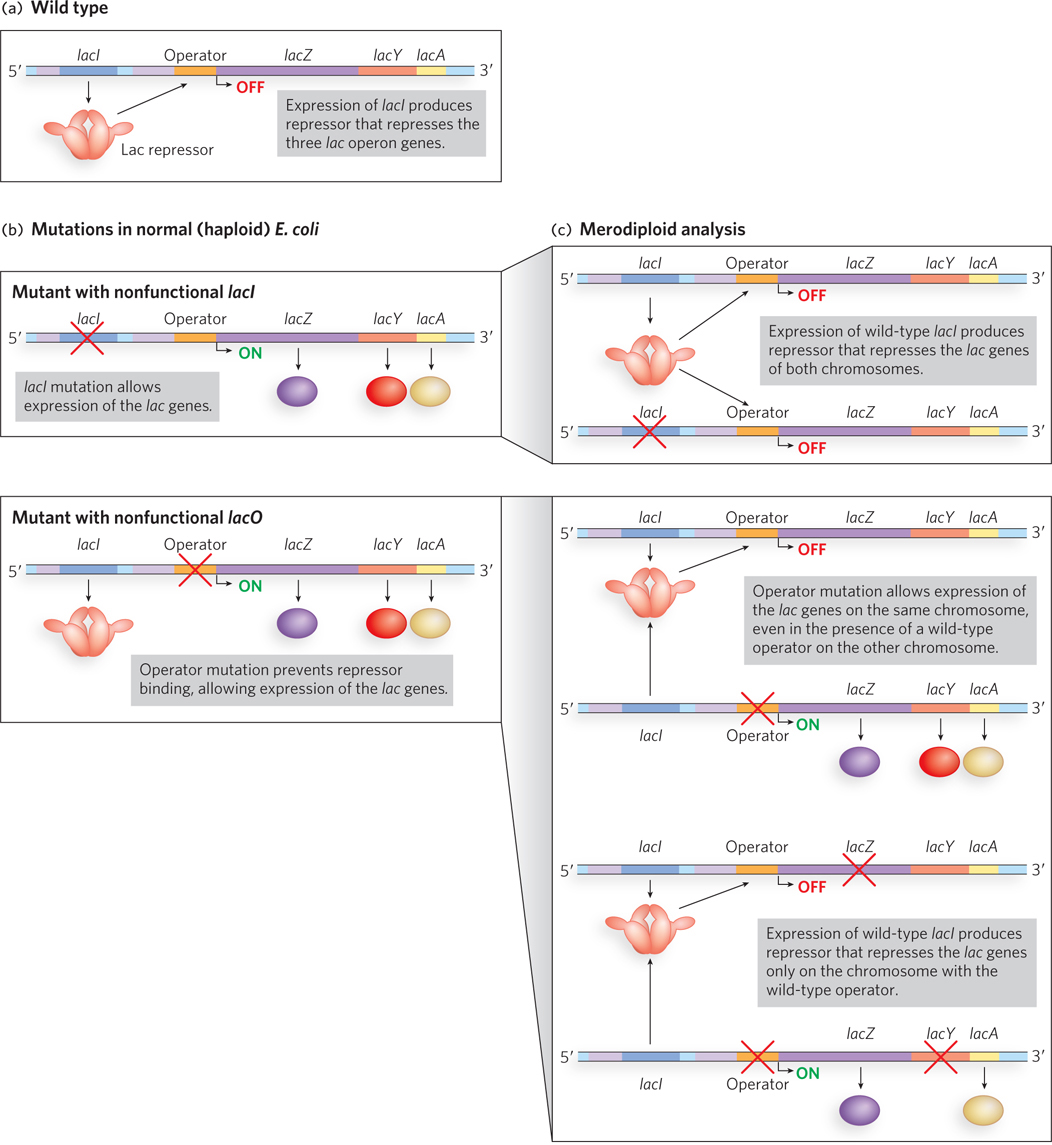
Jacob and Monod’s merodiploid analysis of the lac operon. (a) A simplified view of the wild- d-