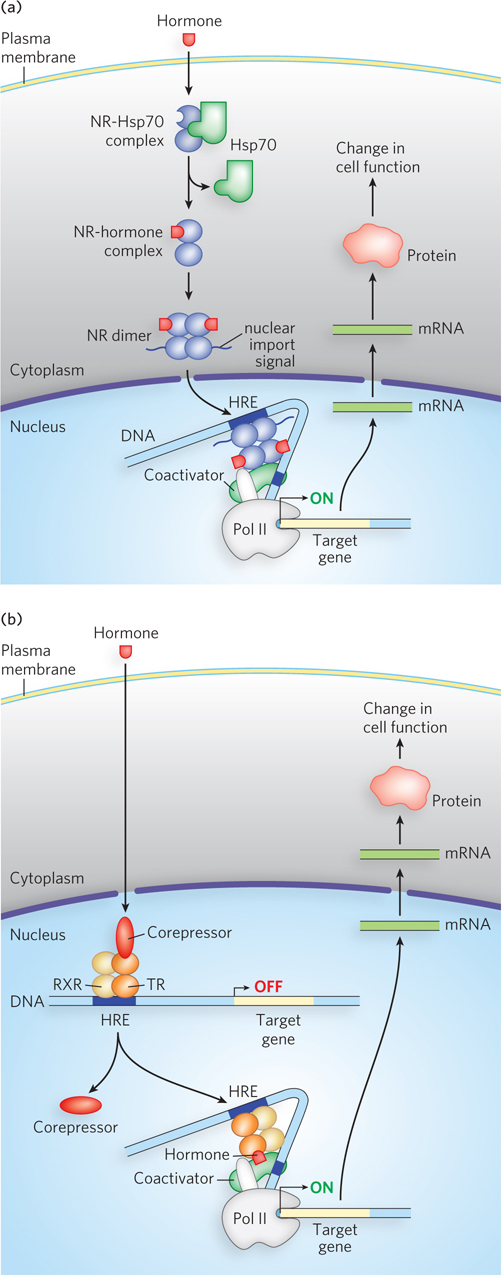
Steroid hormone receptor action. Steroid hormones diffuse across the plasma membrane and associate with a type I or type II nuclear receptor. (a) The type I nuclear receptor (NR), located in the cytoplasm, is complexed with a heat shock protein (Hsp70). Hormone binding releases Hsp70, and the NR dimerizes and exposes a nuclear import signal sequence. The NR-