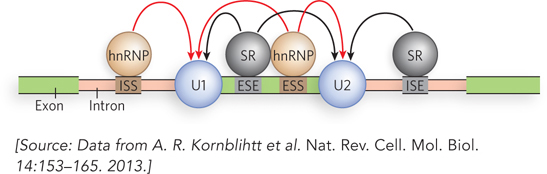
The regulation of splicing. Whether or not an exon is included in the final, mature mRNA transcript in a eukaryotic cell depends on a range of sequences in the primary transcript and the regulatory proteins that bind to them. The sequences that participate in splice site activation are exonic splicing enhancers (ESEs) or intronic splicing enhancers (ISEs), located in the exon or in the adjacent intron. The sequences that participate in splice site silencing are exonic splicing silencers (ESSs) and intronic splicing silencers (ISSs). The most common families of regulatory proteins that bind to these sequences are the serine/arginine-