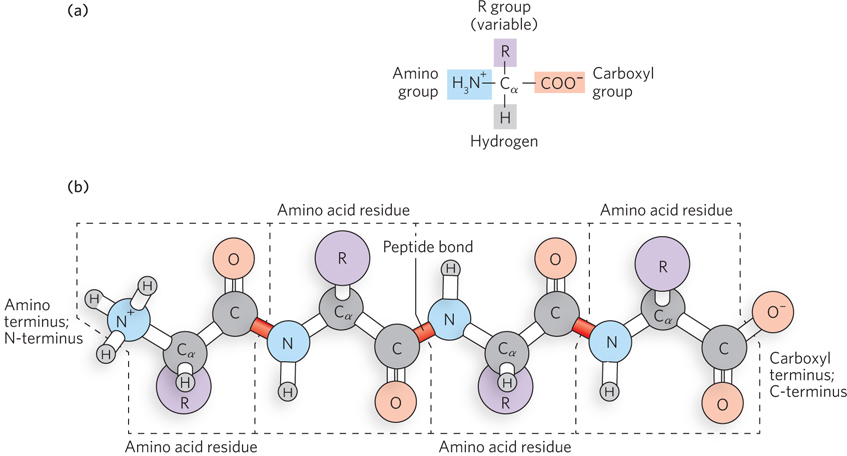
Chemical building blocks of proteins. (a) The structure of an amino acid. The central carbon atom (Cα) bonds to an amino group (blue), a carboxyl group (pink), a hydrogen, and a side chain (R, purple). The amino and carboxyl groups are shown in the ionized forms found in solution at physiological pH. (b) A segment of a polypeptide chain. Note that polypeptide chains have directionality, with a free amino group at one end (the amino terminus, or N- C-