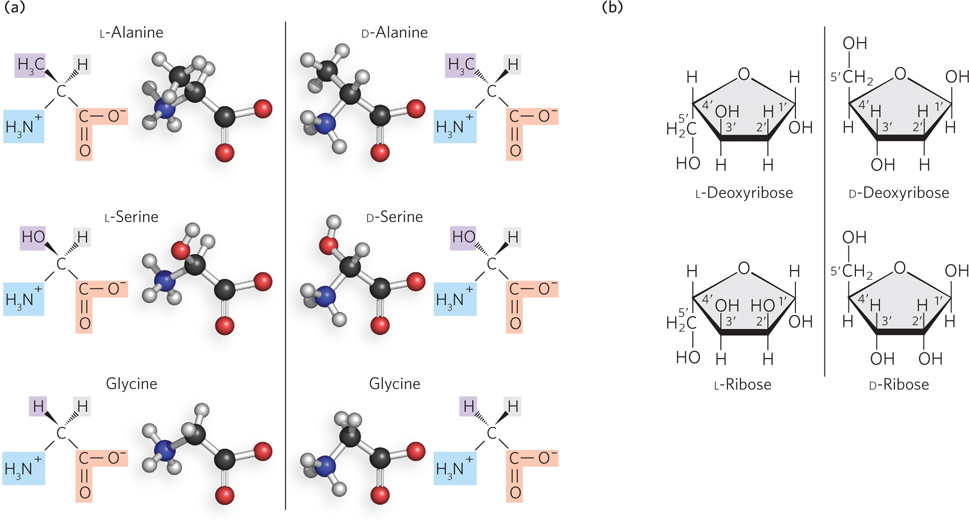
Enantiomers of amino acids and nucleotides. (a) Each amino acid, except glycine, has two possible stereoisomers. These nonsuperposable mirror images (enantiomers) are known as L and D forms. Only the L forms of amino acids are found in natural proteins. (b) All of the carbon atoms in ribose except C- C- C- D- s— D- D- e—