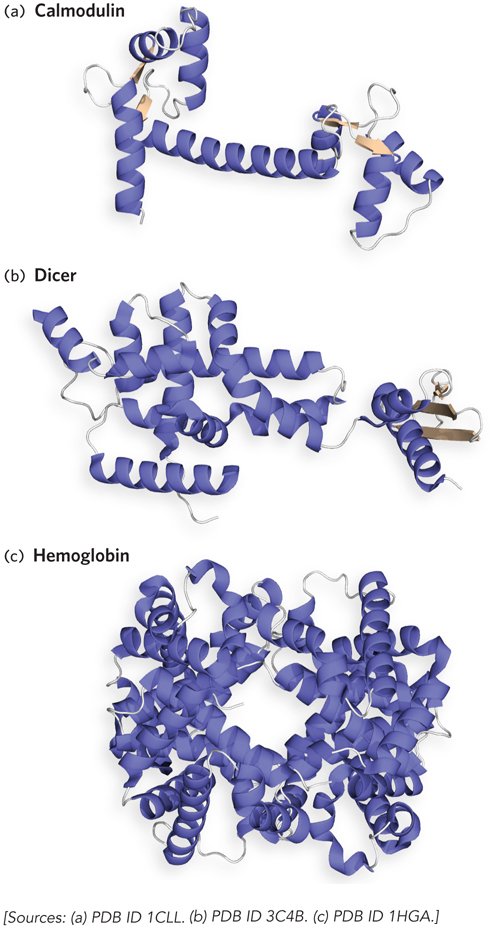
Examples of protein structures. Proteins can form a wide range of three- e- 4-