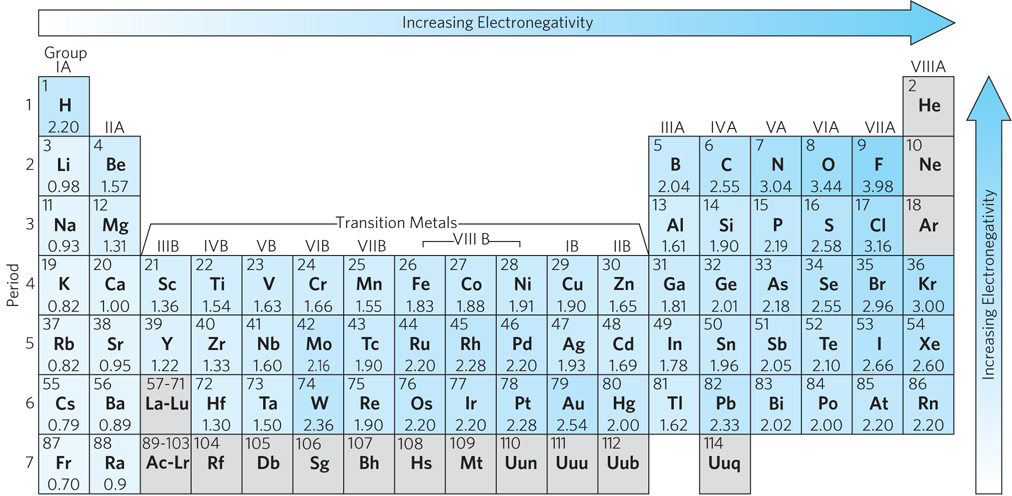
A periodic table of electronegativity, using the Pauling scale. The numbers below each element are the electronegativity values; low values = low electronegativity, and high values = high electronegativity. The electronegativity of an atom is affected by both its atomic weight and the distance of its outer electrons from its positively charged nucleus (i.e., its atomic radius). Electronegativity is affected by the molecular environment of an atom, and hence the electronegativities shown are average values.