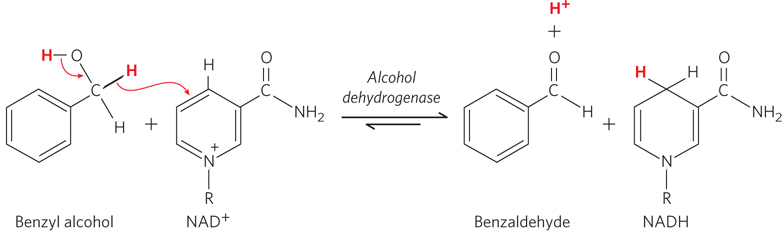
FIGURE 1 Alcohol dehydrogenase, an enzyme essential for metabolizing ethanol and other alcohols, catalyzes the conversion of an alcohol to an aldehyde. The reaction uses a molecule called a cofactor (in this case, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, or NAD+) as a hydrogen atom (proton) acceptor.